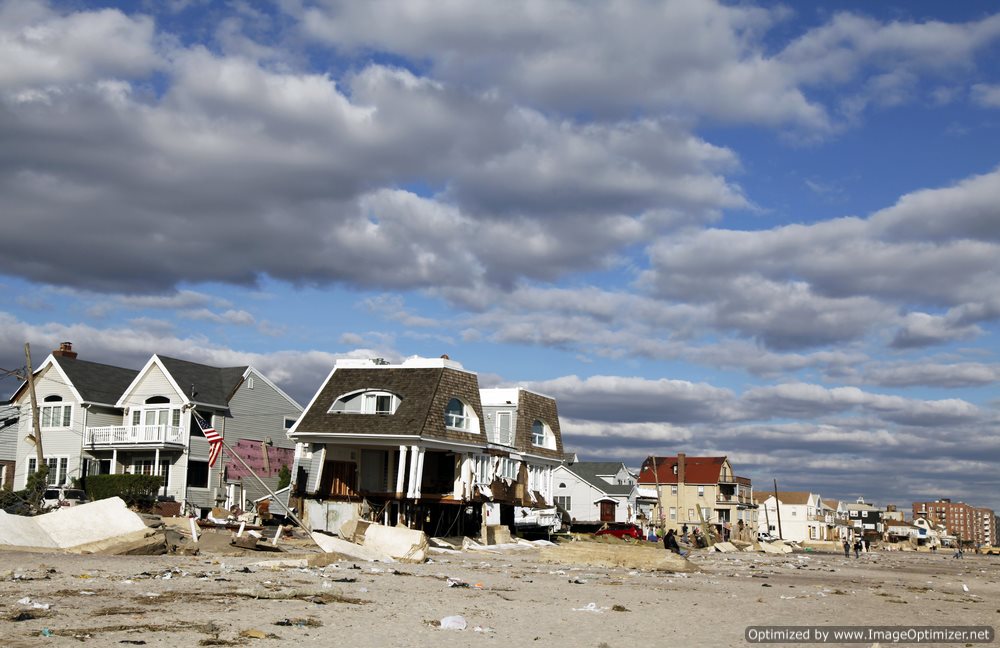
Caught in the Act: WalMart Fined $110 Million for Flouting Environmental Laws




On November 20, 2012, the US Fish & Wildlife Service published its annual appraisal of plants and animals for consideration under the Endangered Species Act (ESA). Since the last review in October of 2011, three species were removed from the status of candidate, two were added, and 9 have changed as far as priority.
A total of 192 species are now recognized as a candidate under the ESA. This is the lowest number in over 12 years. Since the Listing Programs implementation, the 25 candidates have been granted protection under the ESA and proposed protections has occurred for 91 species.
Candidates on the list show signs of being threatened or endangered, but species higher up on the list receive more attention that those lower on the list. Candidates are not protected under the ESA, but their candidacy status helps them receive conservation attention.
Once a species becomes a candidate, the results are provided to landowners and resources managers for the state and local municipalities. The Fish and Wildlife Service is currently involved in conservation agreements covering 5 million acres that help protect 130 species.
The two new candidate species are the Peñasco least chipmunk located in the White Mountains of New Mexico and parts of California and the Cumberland arrow darter in Kentucky and Tennessee. The three species that were removed from the candidacy list are the elongate mud meadow springsnail, the Christ’s paintbrush, and the bog asphodel. The bog asphodel no longer needs protection, and springsnail and paintbrush populations have improved according to the Fish and Wildlife Service.
Dan Ashe, the Fish and Wildlife Service Director, explained the Service’s ultimate goals: “We’re continuing to keep the commitments we made under this agreement, which has enabled us to be more efficient and effective in both protecting species under the ESA, as well as in working with our partners to recover species and get them off the list as soon as possible. Our ultimate goal is to have the smallest Candidate List possible, by addressing the needs of species before they require ESA protection and extending the ESA’s protections to species that truly need it.”
The Fish and Wildlife Service can help protect candidate species in several ways. For one, grant programs provide conservation funds to private landowners as well as states and territories. Secondly, Candidate Conservation Agreements (CCAs) make sure public and private parties perform their share of conservation efforts—like removing threats to the species or stabilizing the specie’s environment. Candidate Conservation Agreements with Assurances (CCAAs) are agreements between the Service and non-Federal landowners.
A complete list of the candidate list can be found on the Fish and Wildlife Service’s website.
Source: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service

The 18th Conference of the Parties of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) began on November 26, 2012. The United Nations has warned that strict policies and pledges are required during the conference to keep temperatures from rising more than 2 degrees Celsius by the end of the century.
Without the emergency adoption of tighter emissions controls, the world’s temperature could increase as much as 5 degrees Celsius by 2100, putting water security, food security, economic security, and human security at risk—especially along coastal cities.
Conservation International (CI), headquartered in Washington, D.C, indicates the conference needs to address at least three areas to curb the impending realization and risks of rising global temperatures.
For one, the conference needs to add to the Kyoto Protocol (the only international emissions treaty) to reach international goals by 2015.
Secondly, new public funding needs to come from developed countries to help developing countries adopt infrastructure and policies to reduce climate change.
Thirdly, the conference needs to allow developing countries to add to existing actions that reduce the destruction of natural environments. CI notes that specific action needs taken in REDD+ areas (Reducing Emissions form Deforestation and Forest Degradation). These areas receive compensation for keeping forested areas protected and reducing emissions associated with deforestation.
Dr. Fred Boltz, the Senior Vice-President for International Policy at CI, reported on the three imperative goals at the conference: “These are the pillars of a successful plan to stabilize the climate, one with increased commitment for immediate actions to avoid catastrophic levels of global warming, and which harnesses the power of nature itself to ensure that humans and all species may adapt to climate change.”
Boltz went on to say, “This year’s conference is crucial because many of the negotiations which have been taking place since 2007 will draw to a close. We need to make sure the progress that has been made over the past five years is not lost.”
The “progress” that Boltz refers to is funding made from developed countries in Copenhagen in 2009. The $30 billion that was pledged is expiring at the end of December, 2012, and no pledges have agreed to continue the funding. The goal was to pledge $100 billion internationally per year by 2020.
Conservation International is now asking for $60 billion in pledges from 2013 to 2015 that will double the “fast start” funds agreed to in Copenhagen.
Boltz raised concern over the lack of pledges: “The debt problems facing several wealthy nations make it more challenging for them to put money on the table. But, if funding is not provided now, the future costs of inaction will be prohibitive in both financial and human terms.”
Source: Conservation International

On November 21, 2012, the Agency for International Development (USAID) announced it is providing more support for Project Predator under INTERPOL. Project Predator helps the South Asia Wildlife Enforcement Network (SAWEN) protect wild tigers.
The U.S. Ambassador to India and Bhutan Nancy Powell made the announcement at the Second Asian Ministerial on Tiger Conservation. The event is organized annually by the Royal Government of Bhutan and the Global Tiger Initiative.
Ministers that attended the Second Asian Ministerial on Tiger Conservation were from 13 different countries containing wild tiger populations. The recent meeting focused on important achievements in conservation and the implementation of a 12-year conservation strategy and ensured political support would continue.
The same countries that attended this year’s meeting approved the Global Tiger Recovery Program (GTRP) during 2010 in Russia.
Ambassador Powell stated: “Protecting our living natural resources, especially endangered species, has increasingly become an issue impacting the security of nations because of massive upsurges in international wildlife trafficking. We need to recognize wildlife crime as a serious crime that undermines good governance and rule of law.”
Project Predator is an initiative crated by INTERPOL that aids in the conservation of wild tigers while respecting countries’ rules and government. Since its creation, the project has provided seminars on police, customs, and wildlife. The seminars have helped enforcement agencies in other countries identify signs of tiger poaching and underground trading.
David Higgins, the manager of the Environmental Crime Programme under INTERPOL, stated: “This additional financial support from USAID will assist INTERPOL's global and regional networks of national police and enforcement agencies in their continued efforts support the tiger range countries in ensuring that we protect the wild tiger population and target those criminals who are attempting to undermine efforts to conserve this iconic species.”
In 2011, USAID provided monetary support for the creation and launch of Project Predator. The project has helped Bhutan, China, India, and Nepal confront the killings of protected tigers in their countries. So far, the countries have made 40 arrests and seizures of big cat skins and other body parts.
Mary Melnyk, the Senior Advisor of Natural Resources Management for Asia and the Middle East for USAID, stated: “USAID is supporting INTERPOL not only because of its international network and communications systems to track down criminals, but also to encourage the greater participation of police in cracking down on wildlife crime.”
Source: Agency for International Development

On November 26, 2012, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommended that states need to harness new and improved water quality criteria and testing for recreational water areas. The recommendations were made with favor from a U.S. District Court and requirements under the Beaches Environmental Assessment and Coastal Health Act of 2000.
The new water quality criteria will make sure visitors are protected as they visit beaches and other bodies of water throughout the year. The criteria can better protect the public and quality of water by observing waterborne illnesses more efficiently, measuring water pollution after heavy rainfalls more quickly, and more.
It is important to note that the recommended criteria do not mandate new requirements. The recommendations simply serve as an example of tools that states can choose to adopt in their overall standards and state or territorial environmental protection agencies.
The new criteria provide states and communities with the most updated scientific information about particular areas, particularly public water bodies like beaches. The updated information can help the state or community issue a beach, lake, or stream closure more quickly.
The new criteria were established by the EPA after several scientific and health studies confirmed some waterborne illnesses (including some stomach illnesses) can occur without a fever. The period required for monitoring water samples was reduced from 90 day to 30 days. The new water quality data will create more accurate water trends and improve advisories.
Some of the other recommendations include the following:
· short-term and long-term testing of bacteria levels in water
· improved recommendations for coastal waters to make sure public health is protected equally in coastal and fresh waters
· a quicker water-testing method that allows the state to see if the water is safe within hours
· tools that can predict problems with water quality and find sources of pollution quickly
The increased testing of bacteria levels was recommended because the criteria in 1986 called for a certain amount of testing depending on the beach usage. The new recommendations replaced the testing/intensity standard and recommended a precautionary testing method for states.
Predictive modeling will pair with epidemiological studies and other information like microbial risk assessments to predict outbreaks in the future. The new and faster testing method recommended by the EPA uses a quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and a quick analytical technique to detect a type of bacteria called curable enterococci.
Source: Environmental Protection Agency

On November 19, 2012, the Maine Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) announced it was hiring a Michigan firm and Maine subcontractor to update state mining rules that have not been changed in decades.
The Michigan firm, North Jackson Company, is an environmental and engineering firm located in the Marquette Mineral District. The firm will work with the state DEP over the next 18 months to make changes and provide environmental insight to the mining rules that have not been changed in 20 years. The changes are required by a bipartisan law passed by the state’s 125th Legislature.
The North Jackson Company received a $175,000 contract because they have experience in mineral mining regulations. They have also helped the state of Michigan make changes to their old mining rules. The Maine subcontractor, S.W. Cole Engineering, Inc., with provide consulting in geotechnical engineering, Maine environmental regulations, and landscape information to the Michigan firm.
DEP Commissioner Patricia Aho emphasized that minerals can be recovered in a way that is environmentally sound for the air, land and water—as long as the state’s minding rules are updated.
She also stated: “Our selection of partners with reputations for providing reliable technical information through rigorous science that allows their clients to make sound environmental management decisions demonstrates this process is one we take seriously. We look forward to working with the North Jackson Company and S.W. Cole as we undertake this important work together.”
After the legislature and DEP agreed to update mining rules, a large number of advertisements were sent to members of the National Mining Association and Interstate Mining Compact. The North Jackson Company was selected because they were the most qualified.
The updated rules will address surface water protection and waste rock management as well as ensure that all proposed mining operations prove financially reasonable environmentally and for state citizens.
Commissioner Aho continued: “DEP’s promise is that as this process moves forward, it will be thoughtful and transparent and if mining activity is carried out in Maine as a result of these regulatory updates, it will be done in a responsible, respectful way that helps Maine and its citizens receive the benefits of the resource while also guaranteeing that environmental protections are upheld and subsequent remediation and closure is adequate.”
More information about the updates can be found on the websites of the Maine DEP, North Jackson Company, or S.W. Cole Engineering.
Source: Maine Department of Environmental Protection

New figures show that, energy-saving technologies and a concerted effort in renewables have led to the overall reduction in climate pollution. This drops in climate pollution—even as the U.S. Congress fails to act on climate change in a broad spectrum—brings the United States more than halfway towards President Barack Obama’s goal.
The United States’ carbon dioxide emissions in 2012 fell to their lowest levels since 1994, according to various environmental reports.
Carbon dioxide emissions in the United States fell by 13% in the last five years, due to new energy-saving technologies and a two-fold increase in the practice of renewable energy resources, as confirmed by the Bloomberg New Energy Finance Commission for the Business Council for Sustainable Energy.
This reduction in climate pollution brings the United States more than halfway towards President Obama’s target of reducing emissions by 17% from 2005 levels over the next decade.
By the end of 2012, the United States’ emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases had fallen nearly 11% from the 2005 levels. This drop puts President Barack Obama in a better position to defend his environmental policies and achievements, which often go overlooked in the bitter realm of climate science. Moreover, such statistics may bolster America’s standing with global climate regulations.
Lisa Jacobson, acting President of the Business Council for Sustainable Energy, said these findings exposed the conservative argument that acting on climate change would hinder the economy—carbon emissions are declining while GDP is rising.
The dramatic decrease in Carbon emissions is attributed to the country’s shift in energy production—Coal fell to 18% in 2012 from 22.5% in 2007 of the nation’s energy mix, and oil use also declined.
Thanks to fracking, natural gas production filled the majority of this gape—the United States received 31% of its electricity from gas-fired plants in 2012.
The report also noted that steadily expanding installations of solar, wind, hydro and geothermal energies have led to the significant drop in Carbon emissions. Renewables represented the largest source of new growth last year, reaching $44 billion.
Over this timeframe, total energy use fell by 6.4% since 2007. The bulk of emissions cut were largely due to installing more efficient cooling and heating systems in commercial locations. Other cuts in emissions came from transport, as 488,000 Americans purchased plug-in or hybrid vehicles.
This mix of energy sources proves that the economy can grow as our reliance on carbon-emitting gases declines.
On November 20, 2012, the Department of Energy (DOE) announced it was awarding support for the design and licensing of small modular reactors with the United States. The strategy is parallel with the Obama Administration’s strategy to access every possible source of energy in the United States.
The funding was announced in March of 2012, and the DOE has just announced the recipient of the award. The project is led by Babcock & Wilcox (B&W) along with the Tennessee Valley Authority and Bechtel. If strategies stay the same, the DOE plans to solicit other companies and manufacturers to focus on developing small modular reactor designs and operations.
The investment from the DOE to B&W will help the company receive Nuclear Regulatory Commission licensing requirements and begin commercial operations by 2022. The small modular reactor project will first occur in Tennessee, but the DOE plans to help operations in Indiana, Maryland, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Virginia. All of the projects will help U.S. utilities receive power from low carbon sources while increasing export opportunities and U.S. dominance in the world energy market.
Secretary Chu stated: “The Obama Administration continues to believe that low-carbon nuclear energy has an important role to play in America’s energy future. Restarting the nation’s nuclear industry and advancing small modular reactor technologies will help create new jobs and export opportunities for American workers and businesses, and ensure we continue to take an all-of-the-above approach to American energy production.”
The recent projects stands as the first-ever government investment in the design, implementation, and licensing of small modular reactors. The DOE will invest in about half of the project’s total cost through a five-year cost-share agreement. Babcock & Wilcox will provide the other half of investment, but the specific amounts toward the project are still being decided by the DOE and B&W.
Small modular reactors are about one-third the size of traditional nuclear power plants. The smaller designs increase safety and offer more economically benefits over large nuclear plants. Also, the small modular reactors can be manufactured at factories then transported to the sites were they can basically be plugged in. The designs decreased capitol costs and construction costs for nuclear energy.
Small modular reactors have other benefits as well. Large reactors cannot be used on some small grids, while small modular reactors can provide power to small grids in a cost-effective way. The reactors allow greater flexibility for utilities as demands grow.
Source: Department of Energy
